AI & Automation
Einstein AI, Agentforce, and AI Chain connectors
According to MuleSoft AI documentation and the MAC Project, MuleSoft offers a comprehensive suite of AI connectors:
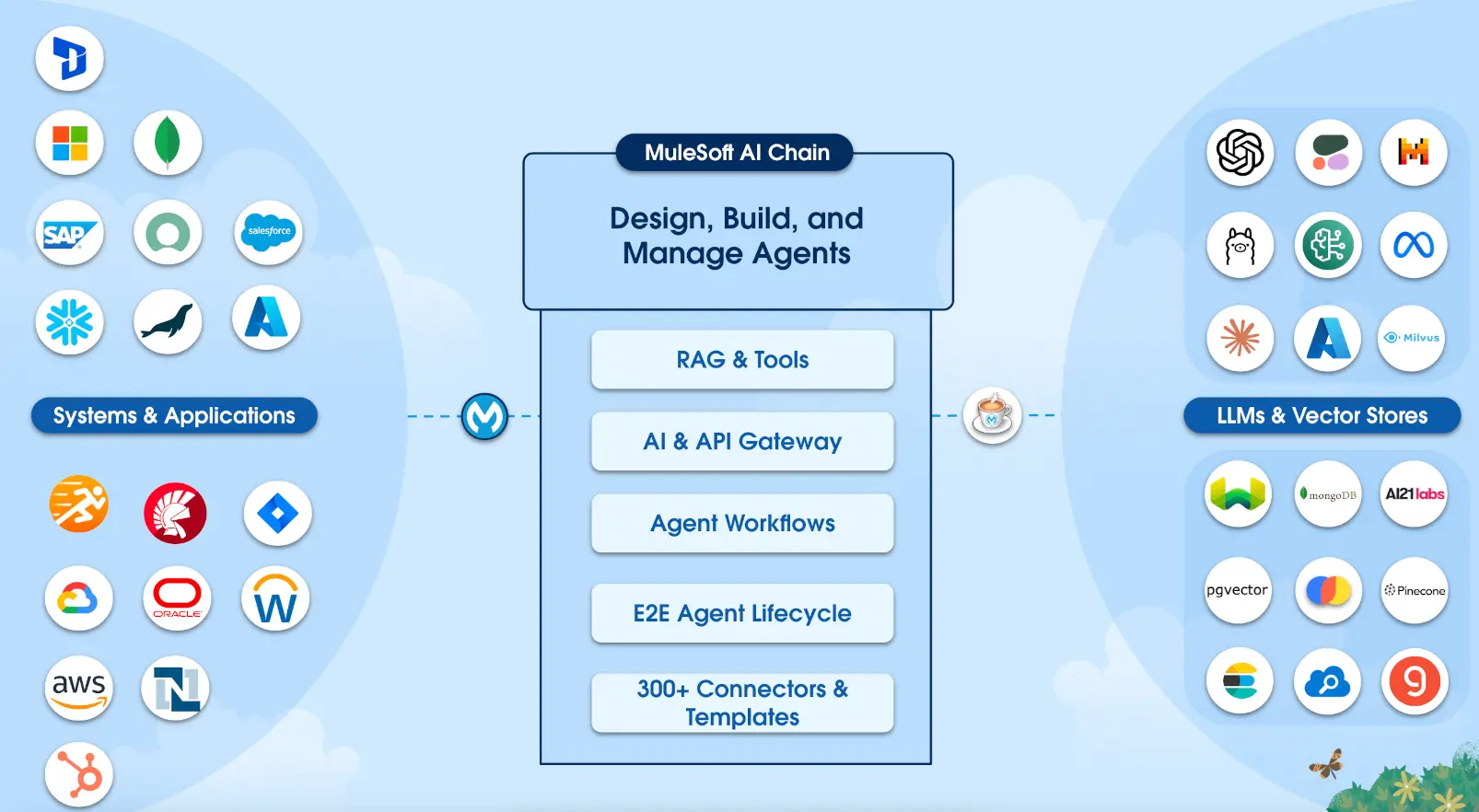
Key AI Connectors:
- Einstein AI Connector: Provides connectivity to LLMs via Salesforce Einstein Trust Layer with built-in security and privacy controls
- Agentforce Connector: Enables integration with AI agents running in Salesforce's Agentforce platform for autonomous task execution
- MuleSoft AI Chain (MAC): Open-source project for orchestrating multiple LLMs, including support for Amazon Bedrock, OpenAI, and more
- Inference & Vector Connectors: Next-generation connectors for AI model inference and vector database operations
According to MuleSoft documentation, the Agentforce Connector provides seamless integration with AI agents running in Salesforce's Agentforce platform:
Key Operations:
- Start Agent Conversation: Establishes connection and initializes the AI agent session
- Continue Agent Conversation: Sends user prompts and receives agent responses
- End Agent Conversation: Gracefully terminates the agent session
Use Cases:
- Surfacing AI agent capabilities in external applications (mobile apps, portals)
- Orchestrating multi-step workflows with autonomous AI decision-making
- Enabling chatbots and virtual assistants powered by Salesforce AI
<!-- Agentforce Connector Example -->
<agentforce:start-agent-conversation config-ref="Agentforce_Config"
agentId="0XxRM000000001"
target="#[vars.conversationId]"/>
<agentforce:continue-agent-conversation config-ref="Agentforce_Config"
conversationId="#[vars.conversationId]"
message="#[payload.userInput]"/>According to the MAC Project documentation and MuleSoft's official blog:
The MuleSoft AI Chain (MAC) project is an open-source initiative to help organizations design, build, and manage AI agents directly within Anypoint Platform. It provides a suite of AI-powered connectors:
| Connector | Purpose | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| AI Chain | Multi-LLM orchestration | Chain prompts, RAG patterns, tool calling |
| Einstein AI | Salesforce Trust Layer | Secure LLM access, data masking |
| Amazon Bedrock | AWS AI models | Claude, Titan, Llama integration |
| MAC Vectors | Vector databases | Embeddings, similarity search |
| MAC WebCrawler | Web scraping for AI | Content extraction for RAG |
